polarimeter organic chemistry|polarimetry diagram : manufacturers Polarimeter: A device used to measure the amount and direction that a substance rotates plane polarized light.A polarimeter consists of a light source, a monochromator (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light), a polarizer . Resultado da Digital Casino. The casino graphics are wonderful, and the feeling of sitting .
{plog:ftitle_list}
5 de out. de 2023 · Dionata Allgayer. -. 5 de outubro de 2023. Patrulha Canina: Um Filme Superpoderoso (Divulgação / Paramount) O filme “ Patrulha Canina: Um Filme .
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course.
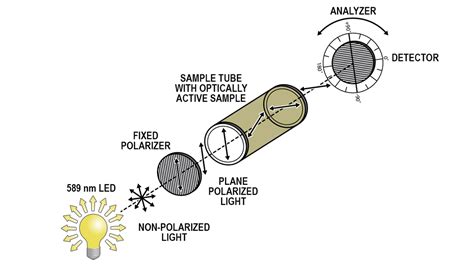
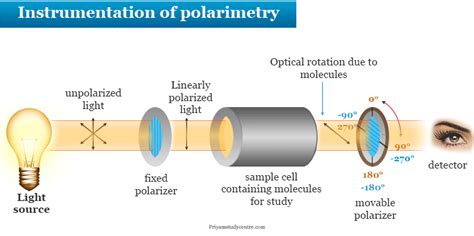
A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., enantiomers. Here is a diagram of a modern polarimeter. Image source: wikipedia. . IUPAC tentative rules for the nomenclature of organic chemistry. Section E. Fundamental stereochemistry IUPAC-IUB Comm. on Biochem. .Polarimeter: A device used to measure the amount and direction that a substance rotates plane polarized light.A polarimeter consists of a light source, a monochromator (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light), a polarizer .When optical rotations are expressed in this standard way, the specific rotation, [α] D, is a physical constant characteristic of a given optically active compound.For example, (+)-lactic acid has [α] D = +3.82, and (−)-lactic acid has [α] D = −3.82.That is, the two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light to exactly the same extent but in opposite directions.
Organic materials typically exhibit optical activity. For instance, the sugar solution exhibits optical rotation when observed through a polarimeter because it is optically active. This property arises from an interaction of the electromagnetic radiation of polarized light with the unsymmetric electric fields generated by the electrons in a . Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. . Raymond, Kenneth W. General Organic and Biological Chemistry. 3rd. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2010. Practice Questions.
Planetary Satellites, Natural. Bonnie J. Buratti, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003 III.A.4 Polarimetry. Polarimetry is the measurement of the degree of polarization of radiation reflected from a satellite's surface. The polarization characteristics depend on the shape, size, and optical properties of the surface particles.Experiment 7: Polarimetric Analysis of Organic Compounds Dzeneta Pajazetovic TA: Nan November 8, 2017. Introduction: The purpose of this experiment is to become familiar with using a polarimeter and to use optical rotation as a method of determining the .
This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .
This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .Source: Vy M. Dong and Diane Le, Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA. This experiment will demonstrate the use of a polarimeter, which is an instrument used to determine the optical rotation of a sample. Optical rotation is the degree to which a sample will rotate polarized light.John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and .
Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. The concentration and physical properties of the solution influence the plane of polarized light and this is detected as the angle of optical rotation by a polarimeter .In previous post, we mentioned that enantiomers (also known as optical isomers) rotate plane-polarised light in opposite directions and are said to exhibit optical activity.So how do we know if an organic molecule rotate plane-polarised light? We use an instrument known as a polarimeter. A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by .Chemistry 350: Organic Chemistry I 5: Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centres 5.3: Optical Activity Expand/collapse global location . A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component .If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Polarimeter: A device used to measure the amount and direction that a substance rotates plane polarized light.A polarimeter consists of a light source, a monochromator (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light), a polarizer (converts the light beam to plane polarized light), a sample tube (holds the sample being measured), a second polarizer (to determine the degree . How optically active compounds rotate plane polarized light.Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/organic .The Polarimeter can be used to measure chiral properties of optically active samples without chemically modifying or destroying the sample. This is a vertical polarimeter that uses a 589 nm LED, a fixed polarizer, and a manually rotated polarizer to detect changes in rotation of plane-polarized light in the presence of an optically active compound. A portion of this solution in a 5-cm Polarimeter tube causes an observed rotation of –1.4 o. Calculate the specific rotation of that compound. . Why Students Seek Organic Chemistry Homework Help and Assignment Help Organic chemistry is one of the most complex and challenging.
Polarimeter: A device used to measure the amount and direction that a substance rotates plane polarized light.A polarimeter consists of a light source, a monochromator (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light), a polarizer (converts the light beam to plane polarized light), a sample tube (holds the sample being measured), a second polarizer (to determine the degree .Polarimeters can be used in kinetics experiments to follow the change in concentration of an optically active sample as a reaction proceeds. Sugars are common examples of optically active compounds. Sucrose is a disaccharide that can be broken down into its two substituent monosaccharides, glucose and fructose. This process occurs too slowly in water to be .
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry. Polarimetry: The measurement and interpretation of optical activity, as measured with a polarimeter. Polarimeter, ca. 1900. A modern electronic polarimeter. Polarimeter components. Related terms: , dextrorotatory .Polarimetry is a common device for distinguishing between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., enantiomers. This makes it a very important instrument in organic chemistry because the optical rotation of a molecule can dictate what reactions it will undergo. This is true for most chiral molecules, including organic, inorganic, and biological compounds. An enantiomer will .Polarimetry is a sensitive, nondestructive technique for measuring the optical activity exhibited by inorganic and organic compounds. A compound is considered to be optically active if linearly polarized light is rotated when passing through it. . 546, 436, 405, and 365nm in a photoelectric polarimeter, have been found to provide advantages . 1. Louis Pasteur And The Discovery Of “Enantiomers” In our last post on optical rotation (See post: Optical Rotation, Optical Activity, and Specific Rotation) we saw that when Louis Pasteur crystallized a salt of a compound then known as “racemic acid” he discovered that it formed two different types of crystals.When redissolved in water, one set of crystals rotated .
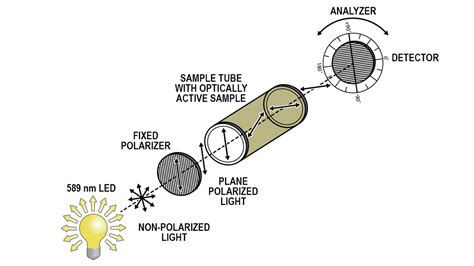
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules). Operation Principle of Polarimeters. The basic operation principle of a polarimeter comprises the following:
what is a polarimetry
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined.
testing chainsaw crank seals
Resultado da BRAZ PRO VPN. P2BRAZ 4.5.8 NEW. P2BRAZ 6.1. P2BRAZ 4.9.1. P2BRAZ (EXCLUSIVO ANDROID 13) Link to everywhere from your bio link.
polarimeter organic chemistry|polarimetry diagram